If Software Update says that your Mac is up to date, then macOS and all of the apps it installs are up to date, including Safari, Messages, Mail, Music, Photos, FaceTime, Calendar, and Books. If you want to update apps downloaded from the App Store, use the App Store to get updates. July 2016 This leaflet explains what a biometric residence permit (BRP) is, what it can be used for, and how employers can check that prospective employees have a right to work in the United Kingdom (UK). The biometric residence permit is proof of the holder's right to stay, work or study in the UK. Mastering the new Word for Mac. After an extended public beta period earlier this year, Microsoft finally took the wraps off Office 2016 for Mac - including the latest version of Word - in July. Media Content - July 2016 Audio files to accompany our articles A directory of all media pages that hold the associated media files for July 2016 audio examples. Part 2: Add Keyboard Layout Language. Open your Word application and go to File - Options. When the Options dialogue box opens, select the Language tab. Under the ' Choose Editing Languages ' section, select your desired language from the drop-down list and click Add. If the Keyboard layout column show ' Not enabled ', then you have to.
'I have a copy of Microsoft Office 2016 on my laptop that is defaulted to the Thai Language. How do I change it to English? Thanks!'
No matter what the default language is, Office can easily be switched to the language of your choice. In this tutorial we'll walk you through the procedure of changing the editing and display language in Microsoft Office 2019 / 2016.
Part 1: Find Your Office Version
The first thing you'll need to do is find your Office version. Open the Word program, click the File tab and choose Account. You'll see which version of Office you're running. For more information such as the architecture of Office, click on the About Word button.
A dialog box opens, showing you the full version number and if you are running 32-bit or 64-bit Office.
Part 2: Add Keyboard Layout Language
Open your Word application and go to File -> Options. When the Options dialogue box opens, select the Language tab. Under the 'Choose Editing Languages' section, select your desired language from the drop-down list and click Add.
If the Keyboard layout column show 'Not enabled', then you have to add the input language to your Windows OS. Just click that link and it will directly open the Language page in the Settings app.
Click the Add a language button.
Find the desired language you want to add, and click Next.
Click the Install button to download the language pack and keyboard for that language.
Luminar flex 1 1 07. Part 3: Add Proofing Tools
If the Proofing column show 'Not installed', then you have to download language accessory pack for spelling and grammar checking. Just click that link and it will open the Language Accessory Pack for Office page with your web browser.
Click the 'Newer versions' drop-down list and select your desired language. The Language Accessory Pack comes with both 32-bit and 64-bit versions. You need to download the appropriate one depending on the architecture of your Office.
After the download is complete, just double-click it and you can go through the installation process in a minute or two.
Part 4: Change Editing and Display Language for Office
Under the 'Choose Editing Languages' section, you should see that the keyboard layout and proofing tools for your desired language are successfully installed. Just select your desired language and click on Set as Default.
Go to the 'Choose Display Language' section to change the language for the display (user interface) and the Help files. Once you're finished, restart Office for the new language to take effect.
Related posts:
Mac Format Uk – July 2016 Torrent
Importing Dates
Dates can be imported from character, numeric, POSIXlt, and POSIXct formats using the as.Date function from the base package.If your data were exported from Excel, they will possibly be in numeric format. Otherwise, they will most likely be stored in character format.
Importing Dates from Character Format
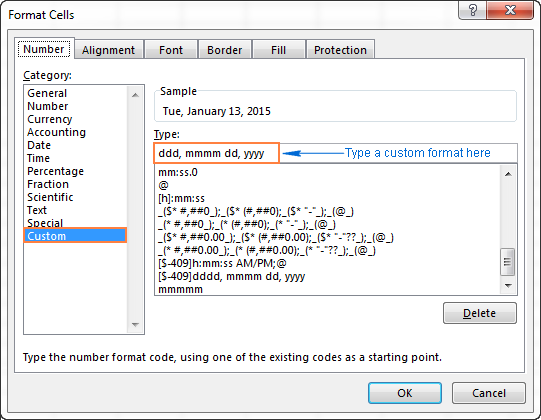

This outputs the dates in the ISO 8601 international standard format %Y-%m-%d. If you would like to use dates in a different format, read 'Changing Date Formats' below.
Importing Dates from Numeric Format
This outputs the dates in the ISO 8601 international standard format %Y-%m-%d. If you would like to use dates in a different format, read the next step:
Changing Date Formats
For example,
Correct Centuries
Purpose of Proper Formatting
Having your dates in the proper format allows R to know that they are dates, and as such knows what calculations it should and should not perform on them. For one example, see my post on plotting weekly or monthly totals. Here are a few more examples:Date Formats
| Conversion specification | Description | Example |
| %a | Abbreviated weekday | Sun, Thu |
| %A | Full weekday | Sunday, Thursday |
| %b or %h | Abbreviated month | May, Jul |
| %B | Full month | May, July |
| %d | Day of the month 01-31 | 27, 07 |
| %j | Day of the year 001-366 | 148, 188 |
| %m | Month 01-12 | 05, 07 |
| %U | Week 01-53 with Sunday as first day of the week | 22, 27 |
| %w | Weekday 0-6 Sunday is 0 | 0, 4 |
| %W | Week 00-53 with Monday as first day of the week | 21, 27 |
| %x | Date, locale-specific | |
| %y | Year without century 00-99 | 84, 05 |
| %Y | Year with century on input: 00 to 68 prefixed by 20 69 to 99 prefixed by 19 | 1984, 2005 |
| %C | Century | 19, 20 |
| %D | Date formatted %m/%d/%y | 05/27/84, 07/07/05 |
| %u | Weekday 1-7 Monday is 1 | 7, 4 |
| %n | Newline on output or Arbitrary whitespace on input | |
| %t | Tab on output or Arbitrary whitespace on input |
References
Mac Format Uk – July 2016 Download
- help(as.Date)
- help(strptime)

